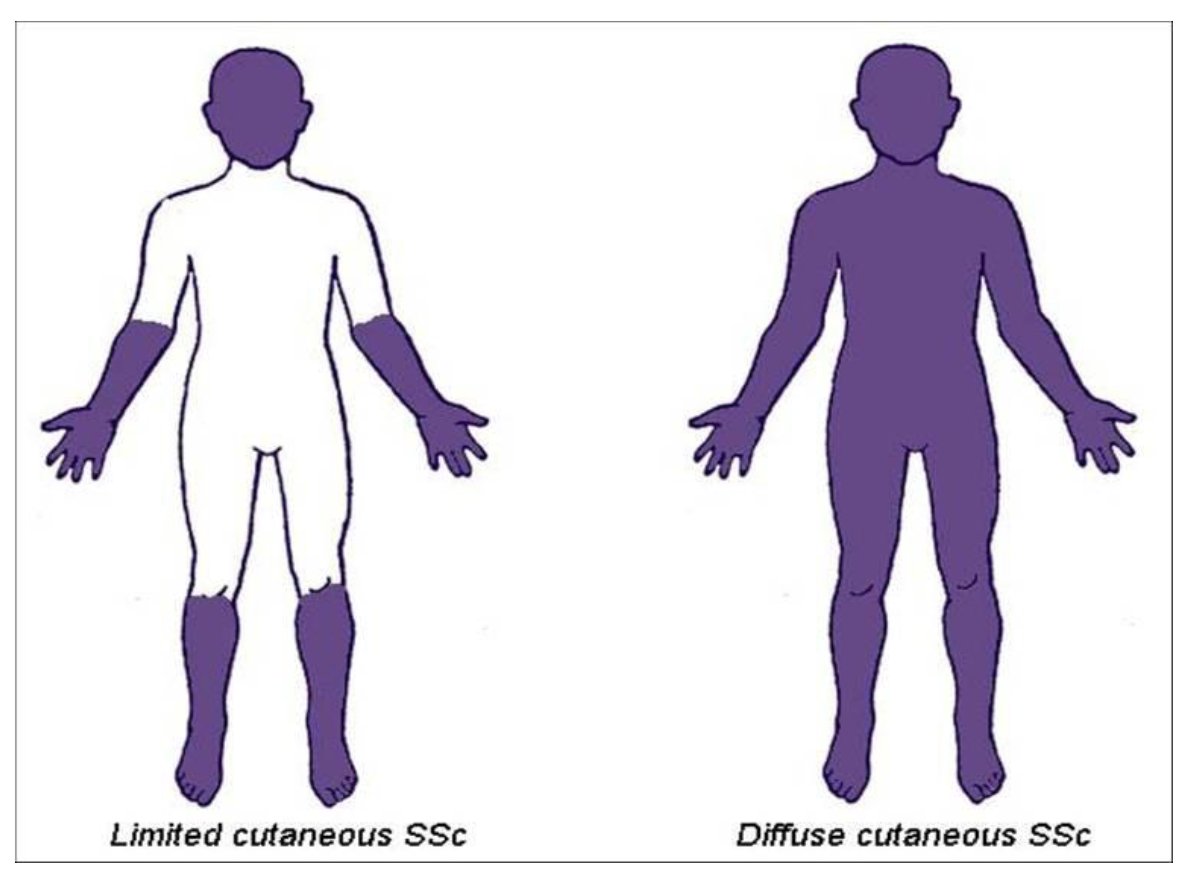
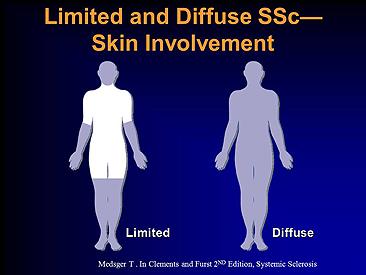
Josh Inglis on X: "Diffuse skin involvement is the most important risk factor. Patients with diffuse cutaneous scleroderma* have early internal organ involvement. * purple is affected skin https://t.co/hoCeufuUoE" / X

A comprehensive framework for navigating patient care in systemic sclerosis: A global response to the need for improving the practice of diagnostic and preventive strategies in SSc - ScienceDirect
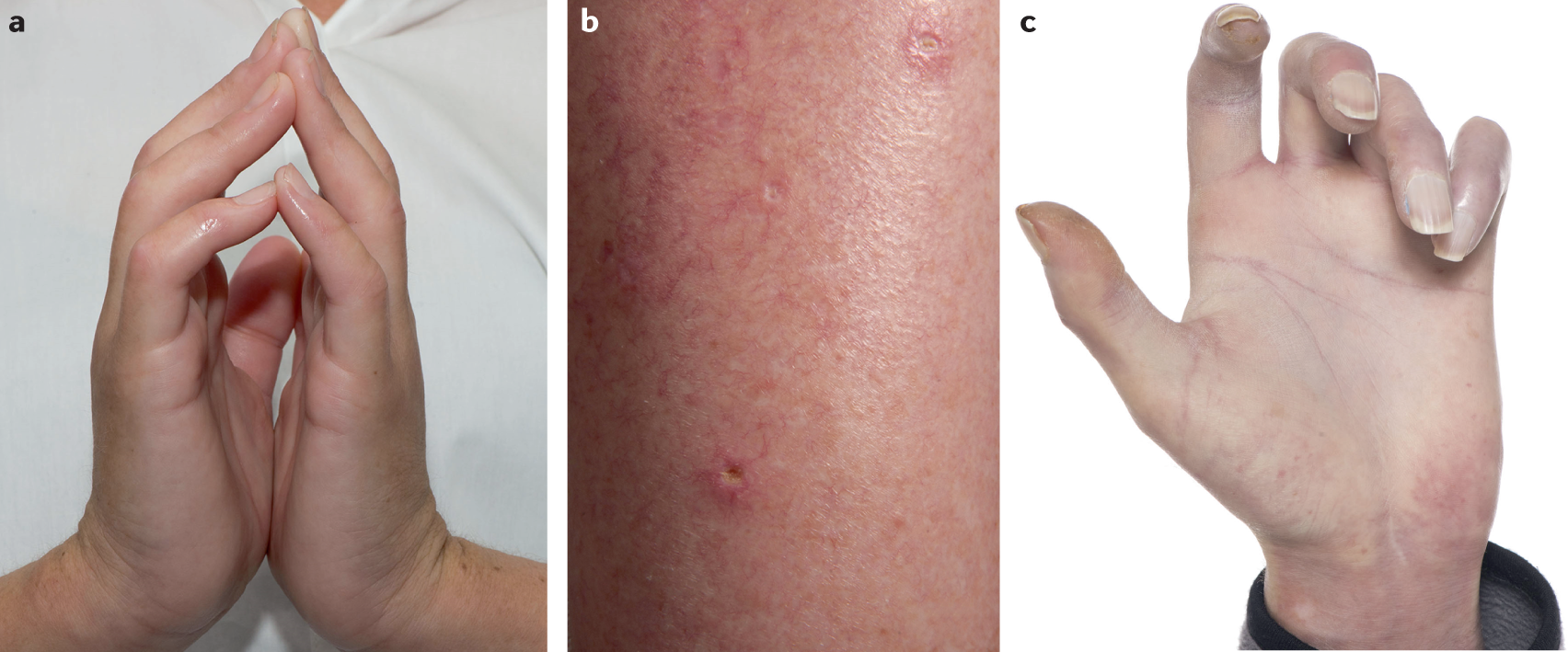
Skin involvement in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis: an unmet clinical need | Nature Reviews Rheumatology


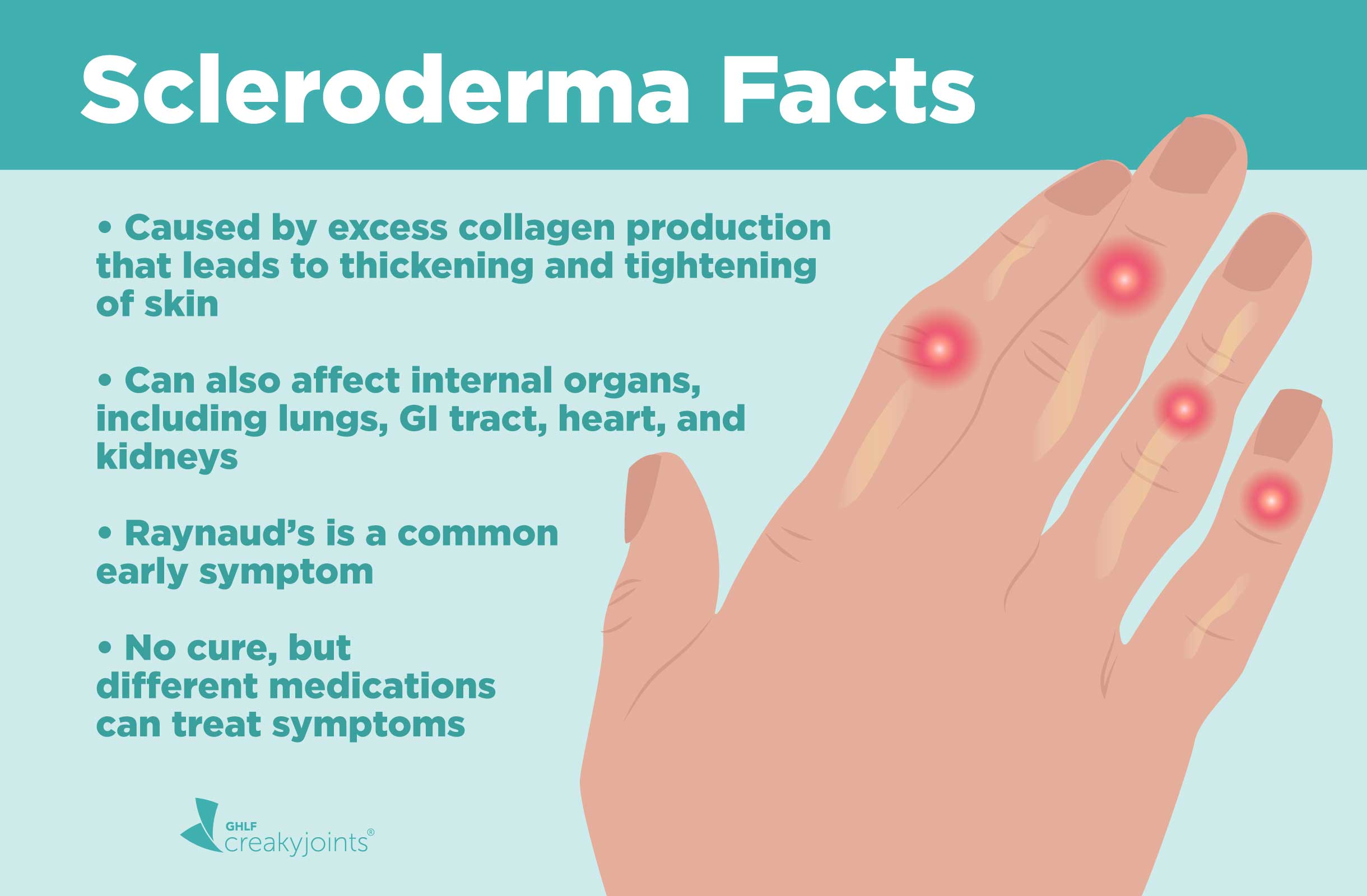


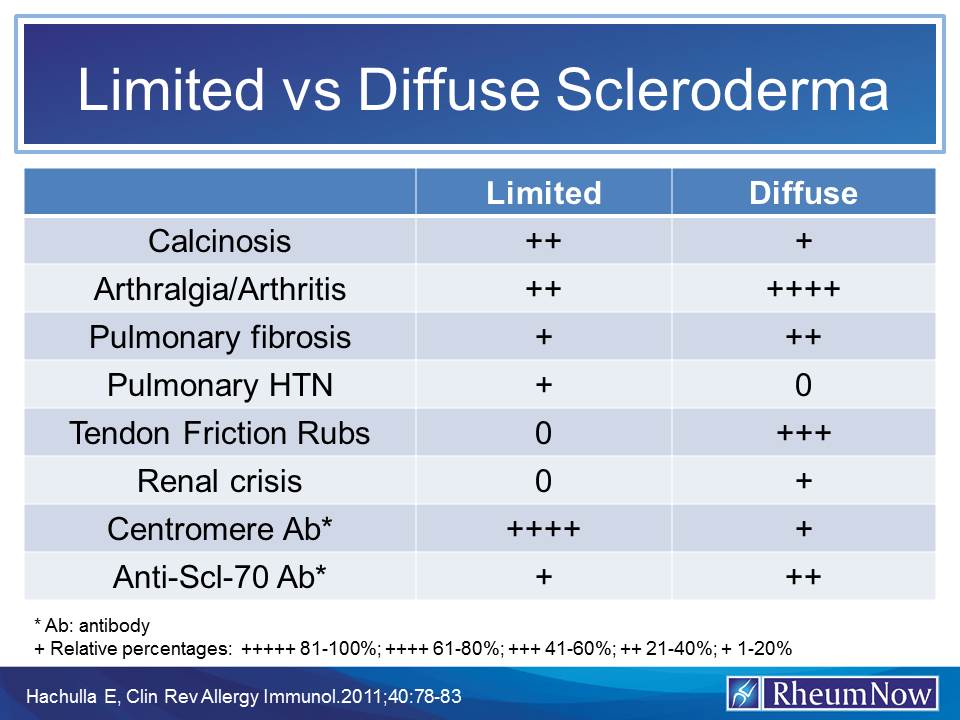
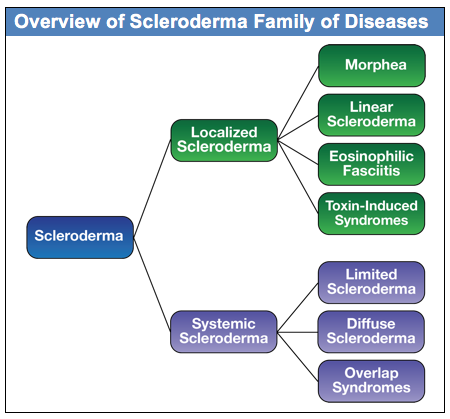


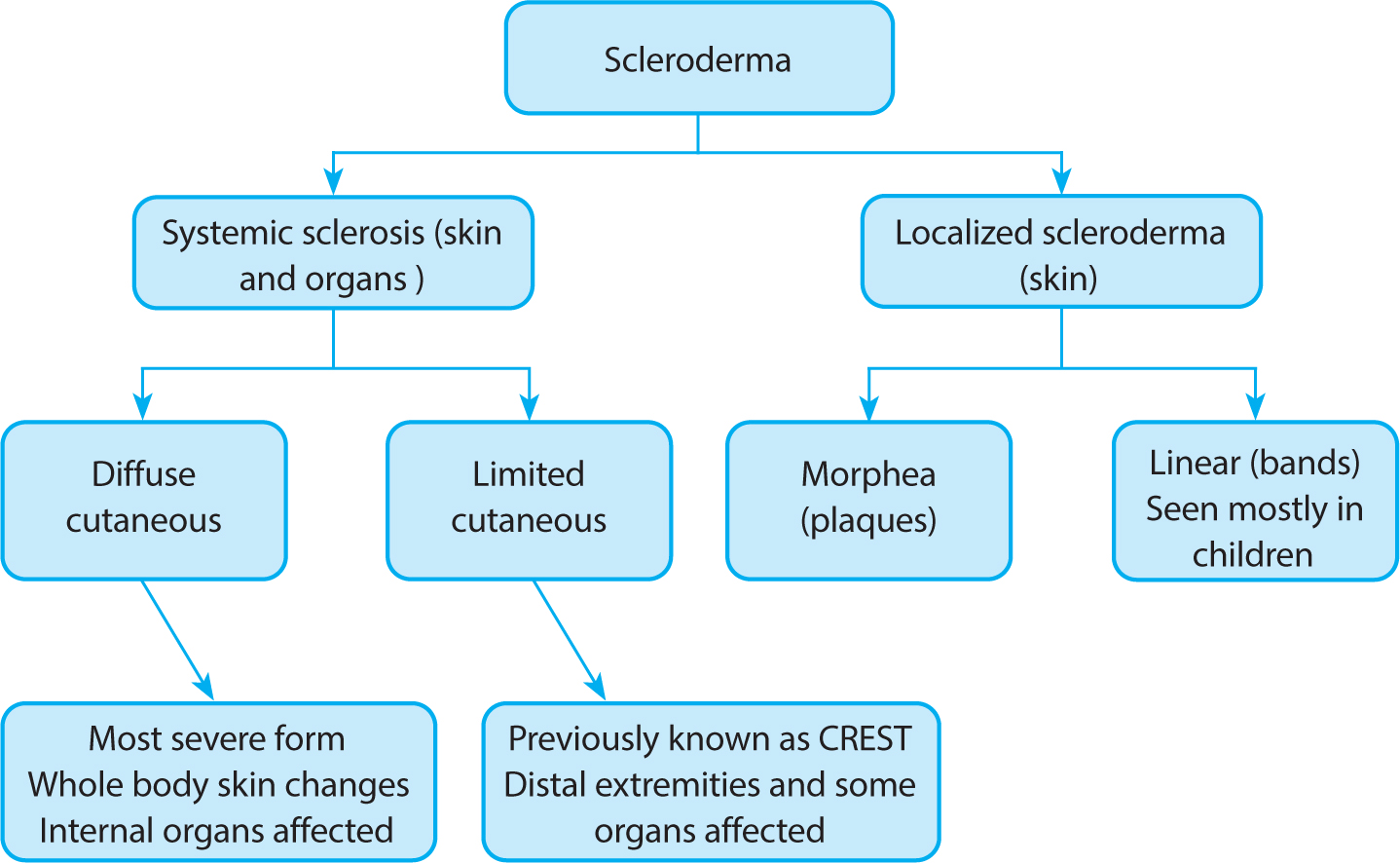



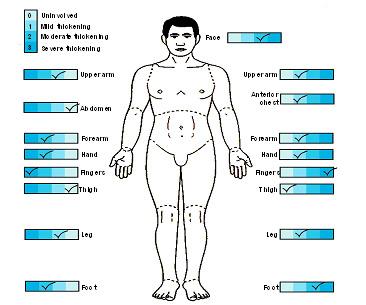
![PDF] Systemic sclerosis/scleroderma: a treatable multisystem disease. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Systemic sclerosis/scleroderma: a treatable multisystem disease. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/6c2e9550daef28537dd16487ce7b6c24f3f82dc0/2-Table1-1.png)
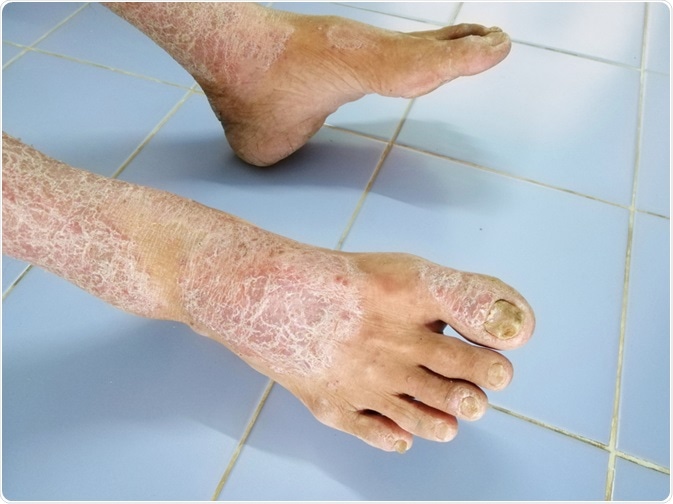
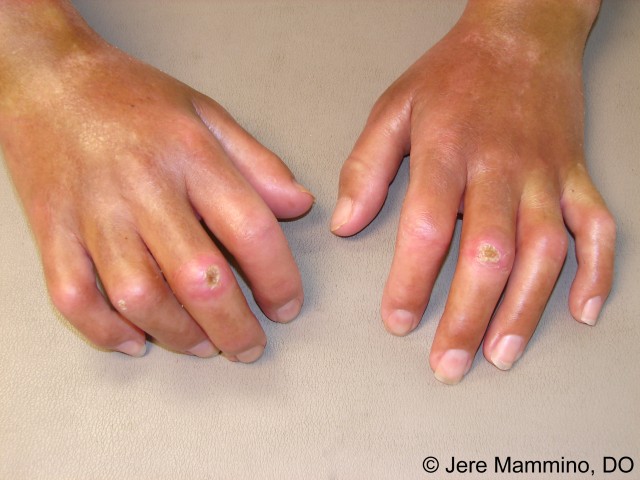
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Scleroderma-resized-56aae71e5f9b58b7d0091456.jpg)

